Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) refers to a wireless system comprised of two components: tags and readers. It is a form of wireless communication that comprises the usage of electromagnetic or electrostatic coupling in the radio frequency portion of the electromagnetic spectrum.

How RFID system works
An RFID system consists of three components: a scanning antenna, a transceiver, and a transponder. When the scanning antenna and transceiver are connected, they are known as RFID readers or interrogators.
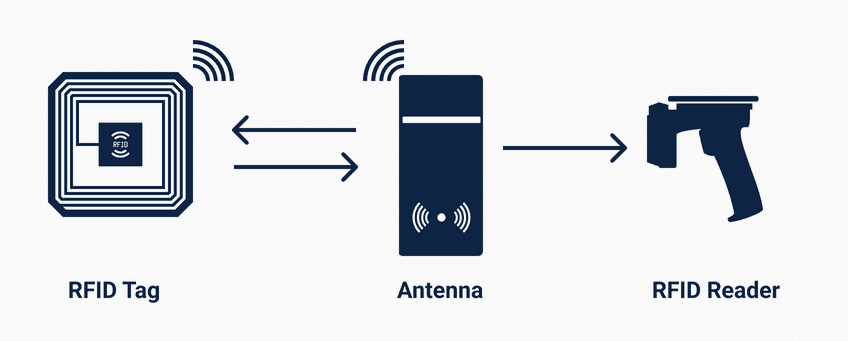
The RFID reader is a network-connected appliance that can be movable or permanently attached. It uses radio waves to send signals that trigger the tag. Once started, the tag sends a wave signal back to the antenna, which is converted into data.
The transponder is present inside the RFID tag. The read content for RFID tags changes based on aspects such as the kind of tag, type of reader, RFID frequency, and interference in the surrounding circumstance. Tags with a more powerful power source also have a more extended read range.
How RFID tags are made of
RFID tags are made of three distinct components: an RFID chip, which is an integrated circuit (IC), an antenna, and a substrate. A tag manufacturer typically does not make all three varieties of components in-house.
Types of RFID Tags
There are various types of RFID tags.
- Active
- Passive
- Semi Passive
- Low Frequency
- High Frequency
- Near Field Communication
- Ultra-High frequency
Active RFID tags
Active RFID tags have a battery and sometimes transmit signals, useful in location search applications. Because the battery in active tags can increase signal strength, they have a longer read range of up to 100 meters.
Passive RFID tags
Passive tags stay inactive until they obtain a radio signal from a reader. The power from the reader’s signal is known to twist the tag and provide an information-carrying signal back to the reader.
Semi-Passive RFID tags
Semi-passive RFID tags include a battery but do not send a periodic signal like active RFID tags. Rather, the battery is only used to change the tag when a signal is obtained. This allows all power from the reader’s signal to be sent back.
Active tags are much more expensive, so they are often only used to track very high-value assets, such as buildings, automobiles, or healthcare tools. Passive tags, mainly ultra-high frequency, and near-field communication, are the most widely used for development and pallet labels.
Low-frequency (LF) RFID tags
Range from 30 kHz to 300 kHz. LF or low-frequency RFID tags have slower read rates and briefer read ranges than UHF or HF, but they’re slightly sensitive to interference by liquids and metals since they have a more extended wavelength. Because of this, they are often used in applications where an RFID label is attached to a metal substrate.
High-frequency (HF) RFID tags
Range from 3 to 30 MHz. HF or High-frequency RFID tags have a longer read range and higher memory abilities, making them well-suited to library media or for use in following bracelets for theme parks. Within the HF RFID category, there is a label called Near field Communication tags.
Near Field Communication RFID tags
NFC tags are a subcategory of HF RFID tags. All Near field Communication tags are HF RFID tags, but not all HF RFID tags are Near Field Communication tags. NFC works in a subset of the high-frequency range such as 13.56 MHz and has significantly further use cases and performance reviews from other RFID classes.
Ultra-high-frequency (UHF) RFID tags
Range from 300 MHz to 3GHz. UHF RFID or ultra-high-frequency tags are known as the supply chain frequency because they are typically lower priced than the additional types, while still supplying good read coverages and rates.
Common applications include item-level search, retail inventory control, and reserve chain efficiencies. It allows them to more accurately determine incoming products by knowing full truckloads of products at a moment.
Cost
- Active tags are $25 and higher
- A passive 96-bit EPC inlay (chip and antenna mounted on a substrate) costs around 0.7 to 15 U.S. cents.
RFID Reader
The RFID reader is a device that can be network-connected. It can either be portable or permanently attached.

Types of RFID readers
Fixed Reader
Fixed readers have ports for antennas that let the reader to be fixed anywhere you want, from ceilings to walls and doorways. For instance, you can review and pay using readers without going to a cashier.
You just walk through an RF zone, and the reader receives the tag data. Handheld readers are portable devices that can be carried any place.
Handheld reader
There are no major differences between a fixed reader and a handheld reader. Fixed readers are stationary while handheld readers are portable. Apart from that, fixed readers gather data from external antennas while handheld readers have antennas built in.
Bluetooth reader
Bluetooth readers can connect seamlessly to tablets, smartphones, or even handheld readers. The Bluetooth technology is used to communicate between an antenna or a reader and a tag attached to the product or item.
RFID Applications
Although RFID technology has been in use for a long time, the demand for RFID equipment is multiplying. Whether or not RFID subordination is needed, applications that presently use barcode technology are suitable candidates for boosting a system that uses RFID or a combination of the two.
RFID offers numerous benefits over the barcode, especially because an RFID tag can carry considerably more data about an object than a barcode scan. Some applications are Inventory management, Asset tracking, Personnel tracking, ID badge, and Supply chain management.
What is RFID Traceability
RFID tracking is a way of automating physical assets' control and locating process. RFID technology is mainly used for traceability applications such as following the origin of development, its establishment, and its journey via the supply chain… all the data is detained in the RFID microchip.
RFID traceability
An RFID label or tag is linked with a special product and will track it throughout its life, from display to storage, transport, and delivery. It is an intelligent label that returns more traditional paperwork. Unlike the barcode label, it qualifies for knowledge storage throughout the product's life and ensures the production process.
RFID technology also lets you instantly locate a product on a display line and know its position within that presentation line.
What is RFID System in warehousing?
With RFID warehouse management software, items can be scanned and cataloged from anywhere, even hidden in boxes or pallets. RFID tags can even be detected and read remotely and simultaneously. With this feature, more than one tag can be read at once.
In a storage environment, an RFID tracking system is a priceless tool. RFID search works via several stages. At each step, stock efficiently reaches under greater control.
A freight arrives at the warehouse receiving port and is unloaded from the truck. An RFID label is attached to the articles in that shipment.
Each tag has interior memory on which an item’s data is stored and changed as it progresses through different processes in the warehouse.
The RFID’s tag can be associated with any object or item with a system that will send the data to the database.
The warehouse control system examines and revises the data as the item moves through the storage system.
Unlike the old barcode method, which used to be expected in the warehousing industry, RFID tags don’t require line-of-sight scanners or reading equipment. Workers no longer need to be within inches of a box to check it manually.
With an RFID storage tracking system, articles can be scanned and cataloged anywhere, even hidden in boxes or pallets.
How RFID can make warehouse management system better
RFID, in conjunction with a WMS, is an excellent real-time business tool that helps manage supply chains, covers goods entry, picking, checking, and delivery better. In addition, it helps with other operations flow & increases profits, and decreases the cost by improving visibility into the Warehouse management system.
-
Reduced Labor Costs: RFID minimizes manual work, which will further help reduce labor costs. Since the tags automatically generate and report information reduces labor work.
-
Workflow Automation: Due to the speed and accurate precision, several warehouse tasks can be automated.
-
More accuracy: Find more accuracy in picking and packing products increases customer satisfaction
-
Improves Visibility: Visualize real-time stock helps to make further decision
RFID tags used in a warehouse produce several key advantages. For starters, RFID is more precise, reducing the risk of human error. It maintains time with automatic processes that communicate with warehouse software. For example, when an item comes or exits the warehouse, the RFID tag automatically records its arrival and exit.
RFID event helps the benefits that require worker intervention, such as pick and pack. Employees can save hours and improve productivity because RFID completes it feasible to find the accurate location of any item instantly.
By incorporating RFID technology with a warehouse management system, you will reduce your storage handling costs, improve accuracy and maximize the rate at which things get done. In the end, RIFD makes for more efficient storage and more satisfied customers.
RFID standards
There are several policies and specifications for RFID technology, but the prominent normal organizations are International Standard Organization, also known as ISO, Electronics Product Code Global Incorporated (EPCglobal), and International Electrotechnical Commission.
Future use of RFID
RFID systems are becoming increasingly employed to support internet of things deployments. Integrating the technology with smart sensors and Internet technology allows detector data, including temperature, motion, and location to be transmitted wirelessly.





